José Luis Oliveira
Universidade de Aveiro, DETI / IEETA
3810-193 Aveiro, Portugal
jlo@ua.pt
(+351) 234 370 500

The NETDIAMOND Platform is a web-based system designed to record patient information in clinical studies, focused on a cohort of HFpEF patients. The system was designed to easily create a data schema based on groups of clinical data. For each group, the different institutions involved can read/edit the data of their patients. In the end, […]

About
GTO is a toolkit for genomics and proteomics, namely for FASTQ, FASTA and SEQ formats, with many complementary tools. The toolkit is for Unix-based systems, built for ultra-fast computations. GTO supports pipes for easy integration with the sub-programs belonging to GTO as well as external tools. GTO works as LEGOs, since it allows the […]

SCALEUS is a data migration tool that can be used on top of traditional systems to enable semantic web features. This user-friendly tool help users easily create new semantic web applications from scratch. Targeted at the biomedical domain, this web-based platform offers, in a single package, a high-perfomance database, data integration algorithms and optimized text […]

Ann2RDF is an interoperable semantic layer that unifies text-mining results originated from different tools, information extracted by curators, and baseline data already available in reference knowledge bases, enabling a proper exploration using semantic web technologies. This result in a more suitable transition process, in which desired annotations are enriched with the possibility to be shared, […]

The NETDIAMOND Platform is a web-based system designed to record patient information in clinical studies, focused on a cohort of HFpEF patients. The system was designed to easily create a data schema based on groups of clinical data. For each group, the different institutions involved can read/edit the data of their patients. In the end, […]
The DICOM validator is a web-based solution for evaluation the compliance of PACS applications with the DICOM standard. It features the “as-a-service” business model, which allows users to immediately reach their goals without the extensive setup efforts required by similar solutions. The DICOM Validator is also a community-driven initiative, where users all around the world […]
MONTRA is a rapid-application development framework designed to facilitate the integration and discovery of heterogeneous objects which may be characterized by distinct data structures. Initially designed as a framework which allows biomedical researchers to easily set up dynamic workspaces, where they can publish and share sensitive information about their data entities, MONTRA is suitable for […]

DISEASECARD is a public web portal that integrates real-time information from distributed and heterogeneous medical and genomic databases, presenting it in a familiar visual paradigm.

OralCard is an online bioinformatic tool that comprises results from manually curated articles reflecting the oral molecular ecosystem (OralPhysiOme), by merging the experimental information available from the oral proteome both of human (OralOme) and microbial origin (MicroOralOme). OralCard is a key resource for understanding the molecular foundations implicated in biology and disease mechanisms of the oral cavity.
The Human Variome relates to genomic mutations and their effects on particular phenotypes. This critical life sciences research field has grown greatly in recent years, mostly due to the appearance of projects such as the Human Variome Project or the European GEN2PHEN Project. Nonetheless, locus-specific mutation databases and included variants are far from being standardized and widely used in the research community workflow.

GeneBrowser is a web-based tool that, for a given list of genes, combines data from several public databases with visualisation and analysis methods to help identify the most relevant and common biological characteristics. The functionalities provided include the following: a central point with the most relevant biological information for each inserted gene; a list of the most related papers in PubMed and gene expression studies in ArrayExpress; and an extended approach to functional analysis applied to Gene Ontology, homologies, gene chromosomal localisation and pathways.

Dicoogle is an open-source Picture Archiving and Communications System (PACS) archive. Its modular architecture allows the quick development of new functionalities, due to the availability of a Software Development Kit (SDK).

NeoScreen is a bioinformatics software that helps diagnosis tasks in newborn screening programs. The application imports MS/MS raw data, and organizes and maintains all the information along the time in a database, providing a set of patterns that allow the detection of abnormalities in the blood samples. Is is been used, from 2005, to support the Portuguese Newborn Screning Program. Since May 2011, NeoScreen is represented by BMD Software Lda.
A PACS solution for echocardiography laboratories that provides a cost-efficient digital archive, and enables the acquisition, storage, transmission and visualization of DICOM cardiovascular ultrasound sequences.
Organization Measurement (OM) method
About
The complete protein-protein interaction (PPI) network of even the most studied organisms is yet to be fully established. This is mostly due to lack of reliability and accuracy of the high-throughput experimental methods used for PPI identification. PPIs can be conveniently represented as networks, allowing the use of graph theory in their […]
Computational Discovery of Putative Leads for Drug Repositioning Through Drug-Target Interaction Prediction

About
GTO is a toolkit for genomics and proteomics, namely for FASTQ, FASTA and SEQ formats, with many complementary tools. The toolkit is for Unix-based systems, built for ultra-fast computations. GTO supports pipes for easy integration with the sub-programs belonging to GTO as well as external tools. GTO works as LEGOs, since it allows the […]

A survey on data compression methods for biological sequences.
Domains: protein sequences, genomic sequences (reference-free and reference-based) and specific formats (FASTA, FASTQ, SAM/BAM).

Compress and analyze genomic sequences. As a compression tool, GeCo is able to provide additional compression gains over several top specific tools, while as an analysis tool, GeCo is able to determine absolute measures, namely for many distance computations, and local measures, such as the information content contained in each element, providing a way to quantify and locate specific genomic events. GeCo can afford individual compression and referential compression.

Smash is a completely alignment-free method/tool to find and visualise genomic rearrangements. The detection is based on conditional exclusive compression, namely using a FCM (Markov model), of high context order (typically 20). For visualisation, Smash outputs a SVG image, with an ideogram output architecture, where the patterns are represented with several HSV values. It can perform both in small- and large-scale.

EAGLE is an alignment-free method and associated program to compute relative absent words (RAW) in genomic sequences using a reference sequence. Currently, EAGLE runs on a command line linux environment, building an image with patterns reporting the absent words regions (in SVG) as well as reporting the associated positions into a file. EAGLE hast got scripts to run on the current outbreak 99 ebola virus genomes (using the human as a reference), including the download, filtering and processing of the entire data.
MENT is a set of tools for lossless compression of microarray images. These tools can also be used for other types of images such as medical, RNAi, etc. This set of tools are divided into two categories. One where a bitplane decomposition approach is used and the other one where a binary tree decomposition is used.

XS is a skilled FASTQ read simulation tool, flexible, portable (does not need a reference sequence) and tunable in terms of sequence complexity. It has several running modes, depending on the time and memory available, and is aimed at testing computing infrastructures, namely cloud computing of large-scale projects, and testing FASTQ compression algorithms. Moreover, XS offers the possibility of simulating the three main FASTQ components individually (headers, DNA sequences and quality-scores)

SACO is a method to handle the DNA bases and gap symbols that can be found in MAF files. SACO is based on a mixture of finite-context models. Contrarily Hanus et al approach, it addresses both the DNA bases and gap symbols at once, better exploring the existing correlations. For comparison with previous methods, our algorithm was tested in the multiz28way dataset. On average, it attained 0.94 bits per symbol, approximately 7% better than the previous best, for a similar computational complexity.

MAFCO is a lossless compression tool specifically designed to compress MAF (Multiple Alignment Format) files. Compared to gzip, the proposed tool attains a compression gain from ≈ 34% to ≈ 57%, depending on the data set. When compared to a recent dedicated method, which is not compatible with some data sets, the compression gain of MAFCO is about 9%.


DNAatGlance is a program for the detection of large-scale genomic regularities by visual inspection. Several discovery strategies are possible, including the standalone analysis of single sequences, the comparative analysis of sequences from individuals from the same species, and the comparative analysis of sequences from different organisms.

MFCompress is a compression tool for FASTA and multi-FASTA files. In comparison to gzip and applied to multi-FASTA files, MFCompress can provide additional average compression gains of almost 50%, i.e., it potentially doubles the available storage, although at the cost of some more computation time. On highly redundant data sets, and in comparison with gzip, 8-fold size reductions have been obtained.

Variobox is a desktop tool for the annotation, analysis and comparison of human genes. Variant annotation data are obtained from WAVe, protein metadata annotations are gathered from PDB and UniProt, and sequence metadata is obtained from Locus Reference Genomic (LRG) and RefSeq databases. By using an advanced sequence visualization interface, Variobox provides an agile navigation through the various genetic regions.

NCCD is a method and package tool designed to compute the Normalized Conditional Compression Distance.

The mRNA optimiser is a tool that redesigns a gene messenger RNA to optimise its secondary structure, without affecting the polypeptide sequence. The tool can either maximize or minimize the molecule minimum free energy (MFE), thus resulting in decreased or increased secondary structure strength.

EuGene is a gene redesign software. It allows opening and parsing genome files, loading genes into a workspace, and redesign the genes according to many redesign methodologies such as enhancing codon usage, codon context, GC content, hidden stop codons, repeated codons or nucleotides, harmonizing genes to other host species, avoiding deleterious sequences, among others. EuGene is free and auto-updates so you can always be up to the latest features and corrections.

GReEn (Genome Resequencing Encoding) is a tool for compressing genome resequencing data using a reference genome sequence. It overcomes some drawbacks of the recently proposed tool GRS, namely, the possibility of compressing sequences that cannot be handled by GRS, faster running times and compression gains of over 100-fold for some sequences.
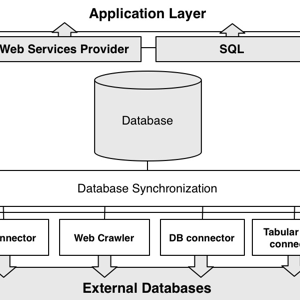
The Genomic Name Server is an innovative data integration system that incorporates a large set of heterogeneous biological data under a simple yet powerful schema. GeNS also addresses the cross-database low identifier coverage issue by proposing a new methodology of data integration.

MIND is a repository of microarray experiments that handles storage, management and analysis of microarray data. It is supported by an infrastructure prepared to integrate dynamically further functionalities (Quality Control assurance, data processing, data mining, visualization, reports, etc.).
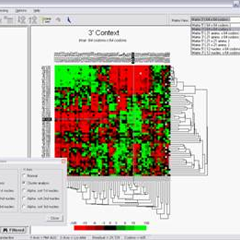
ANACONDA is a software package specially developed for the study of genes’ primary structure. It uses gene sequences downloaded from public databases, as FASTA and GenBank, and it applies a set of statistical and visualization methods in different ways, to reveal information about codon context, codon usage, nucleotide repeats within open reading frames (ORFeome) and others.

SCALEUS is a data migration tool that can be used on top of traditional systems to enable semantic web features. This user-friendly tool help users easily create new semantic web applications from scratch. Targeted at the biomedical domain, this web-based platform offers, in a single package, a high-perfomance database, data integration algorithms and optimized text […]
I2X is a reactive and event-driven framework that simplifies and automates real-time data integration and interoperability. This platform streamlines the creation of customizable integration tasks connecting heterogeneous data sources with any kind of services. Integration is poll-based, with intelligent agents monitoring data sources, or push-based, where the platform waits for data submission by external resources. I2X delivers data […]
Task management systems are crucial tools in modern organizations, by simplifying the coordination of teams and their work. Those tools were developed mainly for task scheduling, assignment, follow-up, and accountability. On the other hand, scientific workflow systems also appeared to help putting together a set of computational processes through the pipeline of inputs and outputs […]

The EU-ADR Web Platform helps experts in the study of adverse drug reactions (ADRs) through the use of computational services and scientific workflows, provided by several European partners. This system assists in the earlier detection of adverse drug reactions, improving drug safety and contributing to public health benefit.

Ipsa scientia potestas est. Knowledge itself is power.
Next-generation Semantic Web Application Framework.

Ann2RDF is an interoperable semantic layer that unifies text-mining results originated from different tools, information extracted by curators, and baseline data already available in reference knowledge bases, enabling a proper exploration using semantic web technologies. This result in a more suitable transition process, in which desired annotations are enriched with the possibility to be shared, […]

Egas is a web-based platform for biomedical text mining and collaborative curation, supporting manual and automatic annotation of concepts and relations.

BeCAS is a web application, API and widget for biomedical concept identification. It helps researchers, healthcare professionals and developers in the identification of over 1,200,000 biomedical concepts in text and PubMed abstracts.

Neji is a innovative and powerfull framework for faster biomedical concept recognition. It is open source and built around four key characteristics: modularity, scalability, speed, and usability. Neji integrates modules of various state-of-the-art methods for biomedical natural language processing (e.g., sentence splitting, tokenization, lemmatization, part-of-speech tagging, chunking and dependency parsing) and concept recognition (e.g., dictionaries and machine learning). The most popular input and output formats, such as Pubmed XML, IeXML, CoNLL and A1, are also supported.

Gimli is an open source, high-performance and multi-corpus solution for automatic recognition of biomedical names. It uses Conditional Random Fields (CRFs) with a rich set of features, applying a method to combine different CRF models. Gimli achieves an F-measure of 87,54 on GENETAG and 73,05 on JNLPBA corpus, significantly outperforming existing open and closed source solutions.

Totum is a innovative harmonisation solution for biomedical annotations, which uses Conditional Random Fields trained on several manually curated corpora. It avoids the single corpus dependency, supporting several biomedical domains and organisms. In the end, Totum harmonises annotations provided by several heterogeneous NER and normalisation solutions, following the gold standard requirements and guidelines.
QuExT (QUery EXpansion Tool) is designed to aid researchers find relationships between genes. It works through expanding each gene name into several associated terms and then querying a custom-designed PubMed index for scientific publications that refer to any of these terms.