- R. Lebre, M. Pedrosa, C. Costa
“A safe architecture for authorisation grant in healthcare ecosystems”
In ICHI 2020 – IEEE International Conference on Healthcare Informatics 2020, Oldenburg, Germany, December 2020.
- A. Trifan, R. Antunes and J. L. Oliveira
“Machine learning for depression screening in online communities”
In 14th International Conference on Practical Applications of Computational Biology & Bioinformatics, PACBB 2020, L’Aquila, Italy, October 2020.
- R. Lebre, E. Pinho, J. M. Silva, C. Costa
“Dicoogle Framework for Medical Imaging Teaching and Research”
In ICTS4eHealth 2020 – IEEE International Workshop on ICT Solutions for E-Health, Rennes, France, June 2020.
- A. Trifan, R. Antunes, S. Matos and J.L. Oliveira
“Understanding depression from psycholinguistics patterns in social media texts”
In ECIR2020 – European Conference on Information Retrieval, Lisbon, Portugal, April 2020.
- T. Almeida and S. Matos
“Calling Attention to Passages for Biomedical Question Answering”
In ECIR2020 – European Conference on Information Retrieval, Lisbon, Portugal, April 2020.
- R. Jesus, P. Nunes, R. Lebre, C. Costa
“Role-based architecture for secure management of telepathology sessions”
In MIE2020 – Medical Informatics Europe, Geneva, Switzerland, April 2020.
- A. Trifan, D. Semeraro, J. Drake, R. Bukowski and J.L. Oliveira
“Social media mining for post-partum depression prediction”
In MIE2020 – Medical Informatics Europe, Geneva, Switzerland, April 2020.
- J. R. Almeida, E. Monteiro, L. B. Silva, A. Pazos, J. L. Oliveira
“A Recommender System based on Cohorts’ Similarity”
In The 30th Medical Informatics Europe conference, Geneva, Switzerland, April 2020.
- J.F. Silva, R. Antunes, J.R. Almeida and S. Matos
“Clinical concept normalization on medical records using word embeddings and heuristics”
In The 30th Medical Informatics Europe conference, Geneva, Switzerland, April 2020.
- J. R. Almeida and S. Matos
“Rule-based extraction of family history information from clinical notes”
In The 35th ACM/SIGAPP Symposium On Applied Computing, Brno, Czech Republic, March 2020.
- R. Antunes, J.F. Silva and S. Matos
“Evaluating semantic textual similarity in clinical sentences using deep learning and sentence embeddings”
In The 35th ACM/SIGAPP Symposium On Applied Computing, Brno, Czech Republic, March 2020.
- J. R. Almeida, P. Freire, O. Fajarda and J. L. Oliveira
“A Computational Platform for Heart Failure Cases Research”
In Healthinf 2020 – International Conference of Health Informatics, Valletta, Malta, February 2020.
- J. R. Almeida, J. F. Silva, A. Sierra, S. Matos and J. L. Oliveira
“Enhancing Decision-making Systems with Relevant Patient Information by Leveraging Clinical Notes”
In Healthinf 2020 – International Conference of Health Informatics, Valletta, Malta, February 2020.
- P. Nunes, R. Jesus, R. Lebre and C. Costa
“Data and Sessions Management in a Telepathology Platform”
In Healthinf 2020 – International Conference of Health Informatics, Valletta, Malta, February 2020.
- A.J. Neves, R. Ribeiro and J. L. Oliveira
“Image Selection based on Low Level Properties for Lifelog Moment Retrieval”
In 12th International Conference on Machine Vision, ICMV 2019, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, November 2019.
- M. Pedrosa, A. Zúquete and C. Costa
“Pseudonymisation with break-the-glass compatibility for health records in federated services”
In 19th IEEE International Conference on BioInformatics and BioEngineering (IEEE BIBE 2019), Athens, Greece, October 2019.
- F.S. Silva and R. Lebre
“Automated pattern recognition of Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy patients”
In RecPad2019, Porto, Portugal, October 2019.
- J.R. Almeida, P. Freire, O. Fajarda and J. L. Oliveira
“A Weighted Rule-Based Model for File Forgery Detection: UA. PT Bioinformatics at ImageCLEF 2019”
In CLEF 2019 Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum, Lugano, Switzerland, September 2019.
- A. Trifan and J. L. Oliveira
“BioInfo@ UAVR at eRisk 2019: delving into social media texts for the early detection of mental and food disorders”
In CLEF 2019 Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum, Lugano, Switzerland, September 2019.
- D. Canedo, A. Trifan and A.J. Neves
“Focus estimation in academic environments using Computer Vision”
In 9th Iberian Conference on Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis (ibPRIA 2019), Madrid, Spain, July 2019.
- J. R. Almeida and J. L. Oliveira
“GenericCDSS – A Generic Clinical Decision Support System”
In IEEE 32th International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS), Córdoba, Spain, June 2019.
- R. Lebre, R. Jesus, P. Nunes and C. Costa
“Collaborative Framework for a Whole-Slide Image Viewer”
In IEEE 32th International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS), Córdoba, Spain, June 2019.
- M. Pedrosa, C. Costa and J. Dorado
“GDPR impacts and opportunities for computer-aided diagnosis – Guidelines and legal perspectives”
In IEEE 32th International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS), Córdoba, Spain, June 2019.
- E. Pinho, J. Figueira Silva and C. Costa
“Volumetric feature learning for query-by-example in medical imaging archives”
In IEEE 32th International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS), Córdoba, Spain, June 2019.
- R. Lebre, L.B. Silva and C. Costa
“An Accounting Mechanism for Standard Medical Imaging Services”
In 2019 IEEE 6th Portuguese Meeting on Bioengineering (ENBENG), Lisbon, Portugal, February 2019.
- A. Trifan and J. L. Oliveira
“FAIRness in Biomedical Data Discovery”
In Proceedings of the 12th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies, Prague, Czech Republic, February 2019.
- J. R. Almeida, O. Fajarda, A. Pereira and J. L. Oliveira
“Strategies to Access Patient Clinical Data from Distributed Databases”
In Proceedings of the 12th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies, Prague, Czech Republic, February 2019.
- R. Antunes, J. F. Silva, A. Pereira and S. Matos
“Rule-based and machine learning hybrid system for patient cohort selection”
In Proceedings of the 12th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies, Prague, Czech Republic, February 2019.
- A. Teixeira, D. Pratas, A. J. Pinho and R. M. Silva
“Evolutionary insights from the comparative analysis of hominid genomes”
In Proceedings of the 24th Portuguese Conference on Pattern Recognition (RecPad2018), Coimbra, Portugal, October 2018.
- C. Figueiredo, D. Pratas, A. J. Pinho, R. M. Silva
“Identification of antifungal targets using alignment-free methods”
In Proceedings of the 24th Portuguese Conference on Pattern Recognition (RecPad2018), Coimbra, Portugal, October 2018.
- E. Pinho and C. Costa
“Feature Learning with Adversarial Networks for Concept Detection in Medical Images: UA.PT Bioinformatics at ImageCLEF 2018”
In Working notes of CLEF 2018 – Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum, Avignon, France, September 2018.
- A.Trifan and J. L. Oliveira
“A FAIR marketplace for biomedical data custodians and clinical researchers”
In IEEE 31th International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS), Karlstad, Sweden, June 2018.
- J. R. Almeida, J. Guimarães, and J. L. Oliveira
“Simplifying the digitization of clinical protocols for diabetes management”
In IEEE 31th International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS), Karlstad, Sweden, June 2018.
- J. R. Almeida, T. M. Godinho, L. Bastião Silva, C. Costa, and J. L. Oliveira
“Services orchestration and workflow management in distributed medical imaging environments”
In IEEE 31th International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS), Karlstad, Sweden, June 2018.
- J. M. Silva, A. Guerra, J. F. Silva, E. Pinho, and C. Costa
“Face De-Identification Service for Neuroimaging Volumes”
In IEEE 31th International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS), Karlstad, Sweden, June 2018.
- J. F. Silva, J. M. Silva, A. Guerra, S. Matos, and C. Costa
“Ejection Fraction Classification in Transthoracic Echocardiography Using a Deep Learning Approach”
In IEEE 31th International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS), Karlstad, Sweden, June 2018.
- C. Costa, M. Pedrosa, J. M. Silva and S. Matos
“Research PACS for diabetic retinopathy screening”
In Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery Proceedings of the 32nd International Congress and Exhibition (CARS 2018), Berlin, Germany, June 2018.
- J. M. Silva, A. Guerra, J. F. Silva, C. Costa and S. Matos
“A novel 3D-CNN approach for ejection fraction classification in transthoracic echocardiography”
In Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery Proceedings of the 32nd International Congress and Exhibition (CARS 2018), Berlin, Germany, June 2018.
- R. Lebre, T. Godinho, L. Silva and C. Costa
“A performant and fully DICOM compliant Web PACS for Digital Pathology”
In Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery Proceedings of the 32nd International Congress and Exhibition (CARS 2018), Berlin, Germany, June 2018.
- M. Pedrosa, J. M. Silva, S. Matos and C. Costa
“SCREEN-DR – Software architecture for the Diabetic Retinopathy Screening”
In Proceedings of MIE 2018, Medical Informatics Europe, Gothenburg, Sweden, April 2018.
- R. Lebre, L. B. Silva and C. Costa
“Shared Medical Imaging Repositories”
In Proceedings of MIE 2018, Medical Informatics Europe, Gothenburg, Sweden, April 2018.
- F. Maia, L. B. Silva and J. L. Oliveira
“Biomedical Informatics – How to choose the best tool for each task”
In Proceedings of MIE 2018, Medical Informatics Europe, Gothenburg, Sweden, April 2018.
- A. Trifan, J. van der Lei, C. Diaz and J. L. Oliveira
“A Methodology for fine-grained access control in Exposing Biomedical Data”
In Proceedings of MIE 2018, Medical Informatics Europe, Gothenburg, Sweden, April 2018.
- M. Pedrosa, J. Miguel and C. Costa
“Reactive Through Services – Opinionated Framework for Developing Reactive Services”
In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science – Volume 1: CLOSER, Funchal, Madeira, Portugal, March 2018.
- J. R. Almeida, R. Ribeiro, and J. L. Oliveira
“A modular workflow management framework”
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Health Informatics (HealthInf 2018), Funchal, Madeira, Portuga, January 2018.
- O. Fajarda; L. B. Silva, P. Rijnbeek, M. Van Speybroeck, and J. L. Oliveira
“A methodology to perform semi-automatic distributed EHR database queries.”
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Health Informatics (HealthInf 2018), Funchal, Madeira, Portuga, January 2018.
- J. M. Silva, A. Silva and P. Vilela
“Enhanced cerebral vascular segmentation with harmonic constraints”
In 23rd Portuguese Conference on Pattern Recognition, Lisbon, Portugal, October, 2017.
- R. Antunes and S. Matos
“Evaluation of word embedding vector averaging functions for biomedical word sense disambiguation”
INForum 2017 – Atas do Nono Simpósio de Informática, Aveiro, p. 25-30, October 2017.
- S. Matos and R. Antunes
“Identifying Relevant Literature for Precision Medicine Using Deep Neural Networks”
Proceedings of the VI BioCreative Challenge Evaluation Workshop, Bethesda, MA, USA, p. 99-101, October 2017
- R. Antunes and S. Matos
“Biomedical Word Sense Disambiguation with Word Embeddings”
11th International Conference on Practical Applications of Computational Biology & Bioinformatics, Porto, p. 273-279, June 2017
- J.F. Silva, J.M. Silva, E. Pinho and C. Costa
“3D-CNN in drug resistance detection and tuberculosis classification”
In CEUR Workshop Proceedings (Vol. 1866), 2017
- E. Pinho, J. F. Silva, J. M. Silva, C. Costa
“Towards representation learning for biomedical concept detection in medical images: UA.PT bioinformatics in ImageCLEF ”
In CEUR Workshop Proceedings (Vol. 1866), 2017
- P. Sernadela and J. L. Oliveira
“Automated nanopublications generation from biomedical literature”
In IEEE 5th Portuguese Meeting on Bioengineering (ENBENG), Coimbra, Portugal, February 2017
- E. Pinho and C. Costa
“Extensible Architecture for Multimodal Information Retrieval in Medical Imaging Archives”
In International Conference on Signal Image Technology and Internet-based Systems (SITIS), Naples, Italy, November 2016
- A. Santos, S. Matos, D. Campos and J. L. Oliveira
“A Curation Pipeline and Web-Services for PDF Documents”
In Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Semantic Mining in Biomedicine (SMBM 2016), Potsdam, Germany, August 2016
- V. Afreixo, J.M.O.S. Rodrigues, C.A.C. Bastos, R.M. Silva
“Exceptional Symmetry Profile: A Genomic Word Analysis”
In International Conference on Practical Applications of Computational Biology & Bioinformatics (PACBB), Sevilla, Spain, June 2016
- E. Monteiro, P. Sernadela, S. Matos, C. Costa and J. L. Oliveira
“Semantic Knowledge Base Construction from Radiology Reports”
In Proceedings of the 9th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies, Rome, Italy, February 2016
- P. Sernadela, S. Matos, J. L. Oliveira
“Ann2RDF: moving annotations to semantic web”
In 17th International Conference on Information Integration and Web-based Applications & Services (iiWAS 2015), Brussels, Belgium, December 2015
- P. Lopes, L. Bastião and J. L. Oliveira
“i2x: an Automated Real-time Integration and Interoperability Platform”
In Proceedings of the 8th IEEE International Conference on Service Oriented Computing & Applications (SOCA2015), Rome, Italy, October 2015
- D. Pratas, RM. Silva, AJ. Pinho, PJSG. Ferreira
“Detection and visualisation of regions of human DNA not present in other primates”
In Proceedings of the 21st Portuguese Conference on Pattern Recognition, RecPad 2015, Faro, Portugal, October 2015
- S. Matos, D. Campos, R. Pinho, R. Silva, M. Mort, D. Cooper, J. L. Oliveira
“Assisted Mining and Curation of Genomic Variants using Egas”
In Proceedings of the Fifth BioCreative Challenge Evaluation Workshop, Sevilla, Spain, September 2015
- S. Matos, J. Sequeira, D. Campos, J. L. Oliveira
“Identification of chemical and gene mentions in patent texts using feature-rich conditional random fields”
In Proceedings of the Fifth BioCreative Challenge Evaluation Workshop, Sevilla, Spain, September 2015
- S. Matos, A. Santos, D. Campos, J. L. Oliveira
“Neji: a BioC compatible framework for biomedical concept recognition”
In Proceedings of the Fifth BioCreative Challenge Evaluation Workshop, Sevilla, Spain, September 2015
- L. A. Bastiao Silva, C. Días, J. van der Lei, and J. L. Oliveira
“Architecture to Summarize Patient-Level Data Across Borders and Countries”
In Proceedings of MEDINFO 2015, Brasil, August 2015
- E. Coelho, J. P. Arrais, and J. L. Oliveira
“Uncovering Microbial Duality within Human Microbiomes: A Novel Algorithm for the Analysis of Host-Pathogen Interactions”
In Proceedings of the 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC2015), Milan, Italy, August 2015
- J. Arevalo, F. A. Gonzalez Osorio, R. Ramos-Pollan, J. L. Oliveira, and M. A. Guevara López
“Convolutional Neural Networks for Mammography Mass Lesion Classification”
In Proceedings of the 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC2015), Milan, Italy, August 2015
- E. Monteiro, C. Costa, J. L. Oliveira
“A Machine Learning Methodology for Medical Imaging Anonymization”
In Proceedings of the 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC2015), Milan, Italy, August 2015
- E. Pinho, C. V. Ferreira, and Carlos Costa
“Simulation of DICOM traffic in PACS networks using behavior profiles”
In Proceedings of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery (CARS 2015), Barcelona, Spain, June 2015
- S. Matos, J. Sequeira, and J.L. Oliveira
“BioinformaticsUA: Machine Learning and Rule-Based Recognition of Disorders and Clinical Attributes from Patient Notes”
In Proceedings of the 9th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval 2015), Denver, Colorado, USA, June 2015
- T. T. Godinho, L. M. Silva, and C. Costa
“An automation framework for PACS workflows optimization in shared environments”
In Proceedings of the 10th Iberian Conference onInformation Systems and Technologies (CISTI 2015), Aveiro, Portugal, June 2015
- P. Lopes and J. L. Oliveira
“Integration-as-a-service for bioinformatics”
In Proceedings of the 10th Iberian Conference on Information Systems and Technologies (CISTI 2015), Aveiro, Portugal, June 2015
- P. Lopes, P. Sernadela, and J. L. Oliveira
“Towards a knowledge federation of linked patient registries”
In Proceedings of the 10th Iberian Conference on Information Systems and Technologies (CISTI 2015), Aveiro, Portugal, June 2015
- P. Lopes, L. Bastiao, and J. L. Oliveira,
“Challenges and opportunities for exploring patient-level data: Preliminary results”
In Proceedings of the 10th Iberian Conference on Information Systems and Technologies (CISTI 2015), Aveiro, Portugal, June 2015
- P. Sernadela, A. Pereira, and R. Rossetti
“DISim: Ontology-driven simulation of biomedical data integration tasks”
In Proceedings of the 10th Iberian Conference on Information Systems and Technologies (CISTI 2015), Aveiro, Portugal, June 2015
- C. Viana-Ferreira, S. Matos, C. Costa
” Long-Term Prefetching for Cloud Medical Imaging Repositories”
In Proceedings of the 26th Medical Informatics Europe Conference (MIE2015), Madrid, Spain, May 2015
- E. Monteiro, F. Valente, J. L. Oliveira, C. Costa
“A Recommender System for Medical Imaging Diagnostic”
In Proceedings of the 26th Medical Informatics Europe Conference (MIE2015), Madrid, Spain, May 2015
- P. Sernadela, P. Lopes, D. Campos, S. Matos, J. L. Oliveira
“A Semantic Layer for Unifying and Exploring Biomedical Document Curation Results”
In Third International Conference (IWBBIO 2015), Bioinformatics and Biomedical, Granada, Spain, April 2015
- S. Brás, A. Silva, J. Ribeiro, and J. Oliveira
“New Insights in Echocardiography Based Left-Ventricle Dynamics Assessment”
In Third International Conference (IWBBIO 2015), Bioinformatics and Biomedical, Granada, Spain, April 2015
- P. Lopes and J. Oliveira
“An Event-Driven Architecture for Biomedical Data Integration and Interoperability”
In Third International Conference (IWBBIO 2015), Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, Granada, Spain, April 2015
- C. V. Ferreira, S. Matos, and Carlos Costa
“Incremental Learning Versus Batch Learning for Classification of User’s Behaviour in Medical Imaging”
In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on health informatics (HealthInf 2015), Lisbon, Portugal, January 2015
- L. Bastião, C. Costa, and J. L. Oliveira
“Semantic search over DICOM repositories”
In IEEE International Conference on Healthcare Informatics 2014 (ICHI 2014) Verona, Italy. September 2014
- F. Valente, A. Silva, C. Costa, J. M. F. Valiente, C. Suárez-Ortega, M. Guevara
“A dataflow-based appraoch to the design and distribution of medical image analytics”
In Proceedings of 8th Iberian Grid Infrastructure Conference (IBERGRID 2014)”, p. 201-212, Aveiro, Portugal, September 2014
- S. Matos, T. Nunes, and J.L. Oliveira
“BioinformaticsUA: Concept Recognition in Clinical Narratives Using a Modular and Highly Efficient Text Processing Framework”
In Proceedings of the 8th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval 2014), p. 135–139, Dublin, Ireland, August 2014
- T. Godinho, L. Bastião, C. Costa, and J. L. Oliveira
“Multi-provider Architecture for Cloud Outsourcing of Medical Imaging Repositories”
In 25th European Medical Informatics Conference (MIE2014) Istanbul, Turkey, August 2014
- L. Bastião, M. Santos, L. Ribeiro, C. Costa, and J. L. Oliveira
“Screening Radiation Exposure for Quality Assurance”
In 25th European Medical Informatics Conference (MIE2014). Istanbul, Turkey, August 2014
- E. Pinho, L. Bastiao Silva, and C. Costa
“A cloud service integration platform for web applications”
In Proccedings of the International Conference on High Performance Computing & Simulation (HPCS 2014), Bologna, Italy, July 2014
- C. V. Ferreira, and C. Costa
“DICOM traffic generator based on behaviour profiles”
In IEEE International Conference on Biomedical and Health Informatics (BHI 2014), p. 93-96, Valencia, Spain, June 2014
- T. Nunes, S. Matos, and J.L. Oliveira
“Extracting sentences describing biomolecular events from the biomedical literature”
In Proceedings of the 11th International Symposium on Distributed Computing and Artificial Intelligence (DCAI 2014), Salamanca, Spain, June 2014
- L. Bastião, L. Bernoud, C. Costa, and J. L. Oliveira
“NoSQL medical imaging archive: comparison between different implementations”
In IEEE International Conference on Biomedical and Health Informatics (BHI 2014) Valencia, Spain, June 2014
- L. Bastião, M. Santos, C. Costa, and J. L. Oliveira
“Normalizing medical imaging archives for dose quality assurance and productivity auditing”
In IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurement and Applications (MeMeA 2014) Lisbon, Portugal, June 2014
- S. Brás, L. Ribeiro, D. A. Ferreira, L. Antunes, and C. Nunes
“Controlling the Hypnotic Drug (propofol) to maintain a stable depth of Anesthesia, in Dogs”
In Proccedings of IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA 2014), Lisbon, Portugal, June 2014
- R.Correia, S. Brás, A. Silva, J. Mendes, D. A. Ferreira
“Development of new research software for real-time raw electroencephalogram analysis”
In Proccedings of IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA 2014), Lisbon, Portugal, June 2014
- L. Castro, J. L. Oliveira, and R. M. Silva
“Mutation Analysis in Park2 Gene Uncovers Patterns of Associated Genetic Variants”, Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing,
In Proceedings of the 8th Internation Conference on Practical Applications of Computational Biology & Bioinformatics (PACBB 2014), Salamanca, Spain, June 2014
- P. Sernadela, E. van der Horst, M. Thompson, P. Lopes, M. Roos, and J. L. Oliveira
“A Nanopublishing Architecture for Biomedical Data”
In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Practical Applications of Computational Biology & Bioinformatics(PACBB 2014), Salamanca, Spain, June 2014
- F. Barbosa, J. Arrais and J.L. Oliveira
“Weighted Gene Co-expression Network Analysis Applied to Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Data”
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics (ICHI 2013), Vilamoura, Portugal, November 2013
- E. Monteiro, C. Costa, and J. L. Oliveira
“A DICOM viewer based on web technology”
In Proceedings of IEEE 15th International Conference on e-Health Networking, Applications & Services (Healthcom 2013), Lisboa, Portugal, October 2013
- C. V. Ferreira, and C. Costa
“A cloud based architecture for medical imaging services”
In Proceedings of IEEE 15th International Conference on e-Health Networking, Applications & Services (Healthcom 2013), Lisboa, Portugal, October 2013
- L. Ribeiro, F. Honório, J. L. Oliveira, C. Costa
“Leveraging XDS-I and PIX workflows for validating cross-enterprise patient identity linkage”
In Proceedings of IEEE 15th International Conference on e-Health Networking, Applications & Services (Healthcom 2013), Lisboa, Portugal, October 2013
- D. Campos, S. Matos, and J. L. Oliveira
“Chemical name recognition with harmonized feature-rich conditional random fields”
In Proceedings of Fourth BioCreative Challenge Evaluation Workshop, vol. 2, p. 82-87, October 2013
- D. Campos, J. Lourenço, T. Nunes, R. Vitorino, P. Domingues, S. Matos, and J. L. Oliveira
“Egas – Collaborative Biomedical Annotation as a Service”
In Proceedings of Fourth BioCreative Challenge Evaluation Workshop, vol. 1, p. 254-259, October 2013
- L. Bastião, C. Costa, and J. L. Oliveira
“An agile framework to support distributed medical imaging scenarios”
In IEEE International Conference on Healthcare Informatics 2013 (ICHI 2013) Philadelphia, PA, USA. September 2013
- F. Marques, P. Azevedo, J. P. Cunha, M. B. Cunha, S. Brás, and J. M. Fernandes
“IREMAN: FIRefighter team brEathing Management system using ANdroid”
In 17th International Symposium on Wearable Computers (ISWC 2013), Zurich, Switzerland, September 2013
- L. Ribeiro, R. Rodrigues, C. Costa and J.L. Oliveira,
“Enabling Outsourcing XDS for Imaging on the Public Cloud”
In Proceedings of the 14th World Congress on Medical and Health Informatics (MEDINFO 2013), Copenhagen, Denmark, August 2013
- D. Campos, S. Matos, and J. L. Oliveira
“Neji: a tool for heterogeneous biomedical concept identification”
In Proceedings of the BioLINK SIG, ISMB/ECCB, Berlin, Germany, July 2013
- L. Bastiao, S. Campos, C. Costa, and J. L.Oliveira
“Integrating echocardiogram reports with medical imaging”
In 26th IEEE International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS 2013), Porto, Portugal, June 2013
- S. Brás, J. M. Fernandes, and J. P.S. Cunha,
“ECG Delineation and Morphological Analysis for Firefighters Tasks Differentiation”
In Proceedings of the 26th International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS 2013), Porto, Portugal, June 2013
- M. Santos, L. Bastião, C. Costa, A. Silva, and N. Rocha,
“Multi Vendor DICOM Metadata Access: A Multi Site Hospital Approach Using Dicoogle”
In 8th Iberian Conference on Information Systems and Technologies (CISTI 2013), Lisboa, Portugal, June 2013
- T. Godinho, L. B. Silva, C. Viana-Ferreira, C. Costa and J. L. Oliveira
“Enhanced regional network for medical imaging repositories”
In 8th Iberian Conference on Information Systems and Technologies (CISTI 2013), Lisboa, Portugal, June 2013
- V M. Prieto, S. Matos, M. Álvarez, F.Cacheda, and J. L. Oliveira
“Analysing Relevant Diseases From Iberian Tweets”
In Proceedings of the 7th Int. Conf. on Practical Applications of Computational Biology and Bioinformatics (PACBB 2013), Salamanca, Spain, May 2013
- S. Matos, H. Araújo, and J. L. Oliveira
“Structuring and Exploring the Biomedical Literature Using Latent Semantics”
In Proceedings of the 10th International Symposium on Distributed Computing and Artificial Intelligence (DCAI 2013), Salamanca, Spain, May 2013
- J. C. Santos and S. Matos
“Predicting Flu Incidence from Portuguese Tweets”
In Proceedings of the International Work-Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, Granada, Spain, March 2013
- J. C. Santos, T. Pedrosa, C. Costa, and J. L. Oliveira
“Concepts for a Personal Health Record”
In 24th European Medical Informatics Conference (MIE 2012), Pisa, Italy, 2012.
- C. Viana-Ferreira, D. Ferreira, F. Valente, E. Monteiro, C. Costa, and J. L. Oliveira
“Dicoogle Mobile: a medical imaging platform for Android”
In 24th European Medical Informatics Conference (MIE 2012), Pisa, Italy, 2012
- L. Ribeiro, C. Costa, and J. L. Oliveira
“Enhancing the many-to-many relations across IHE Document Sharing Communities”
In 24th European Medical Informatics Conference (MIE 2012), Pisa, Italy, 2012
- E. J. M. Monteiro, L. A. B. Silva, and C. Costa
“CloudMed: Promoting telemedicine processes over the cloud”
In Proceedings of the 7th Iberian Conference onInformation Systems and Technologies (CISTI 2012) 2012
- L. Bastião Silva, C. Costa, and J. L. Oliveira
“A DICOM relay service supported on cloud resources”
In 5th International Conference on Health Informatics (HEALTHINF 2012), Vilamoura, Portugal, 2012
- T. Pedrosa, R. P. Lopes, J. C. Santos, C. Costa, and J. L. Oliveira
“A secury personal health record repository”
In 5th International Conference on Health Informatics (HEALTHINF 2012), Vilamoura, Portugal, 2012
- L. Velte, T. Pedrosa, C. Costa, and J. L. Oliveira
“An OPENEHR repository based on a native XML database”
In 5th International Conference on Health Informatics (HEALTHINF 2012), Vilamoura, Portugal, 2012
- R. Mendonça, P. Lopes, H. Rocha, J. Oliveira, L. Vilarinho, R. Santos, and J. L. Oliveira
“Gathering and managing genotype and phenotype information about rare diseases patients”
In 5th International Conference on Health Informatics (HEALTHINF 2012), Vilamoura, Portugal, 2012
- J. Melo, J.P. Arrais, P. Lopes, N. Rosa, M. J. Correia, M. Barros, and J. L. Oliveira
“OralCard – web information system for oral health”
In 5th International Conference on Health Informatics (HEALTHINF 2012), Vilamoura, Portugal, 2012
- C. Viana-Ferreira, C. Costa, and J. L. Oliveira
“Dicoogle Relay – a Cloud Communications Bridge for Medical Imaging”
In 25th IEEE International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS 2012), Rome, Italy, 2012
- R. Mendonça, A. F. Rosa, J. L. Oliveira, and A. Teixeira
“Towards ontology based health information search in Portuguese – A case study in neurologic diseases”
In 7th Iberian Conference on Information Systems and Technologies (CISTI 2012), Madrid, Spain, 2012
- P. Gaspar, J. Carbonell, and J. L. Oliveira
“Parameter influence in genetic algorithm optimization of support vector machines”
In 7th International Conference on Practical Applications of Computational Biology & Bioinformatics (PACBB 2012), Salamanca, Spain, 2012
- P. Lopes, R. Mendonça, H. Rocha, J. Oliveira, L. Vilarinho, R. Santos, and J. L. Oliveira
“A Rare Disease Patient Manager”
In 7th International Conference on Practical Applications of Computational Biology & Bioinformatics (PACBB 2012), Salamanca, Spain, 2012
- P. Lopes and J. L. Oliveira
“COEUS: A Semantic Web Application Framework”
In Semantic Web Applications and Tools for Life Sciences (SWAT4LS 2011), London, UK, 2011
- S. Matos and J. L. Oliveira
“Prioritizing Literature Search Results Using a Training Set of Classified Documents”
In 5th International Conference on Practical Applications of Computational Biology & Bioinformatics (PACBB 2011), vol. 93, pp. 381-388, 2011.
- P. Lopes and J. L. Oliveira
“Towards Knowledge Federation in Biomedical Applications”
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Semantic Systems (I-Semantics 2011), Graz, Austria, 2011
- P. Lopes and J. L. Oliveira
“A Semantic Web Application Framework for Health Systems Interoperability”
In Proceedings of the first international workshop on Managing interoperability and complexity in health systems (MIXHS 2011), Graz, Austria, 2011
- C. Santos, T. Pedros, C. Costa, and J. L. Oliveira
“On the Use of Openehr in a Portable Phr”, Healthinf 2011: Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics (Healthinf 2011), pp. 351-356, 2011.
- T. Pedrosa, R. P. Lopes, J. C. Santos, C. Costa, and J. L. Oliveira
“Hybrid Electronic Health Records”, Healthinf 2011: Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics (Healthinf 2011), pp. 571-574, 2011.
- D. Campos, D. Rebholz-Schuhmann, S. Matos, and J. L. Oliveira
“A CRF-based approach to harmonize heterogeneous gene/protein annotations”
In Second CALBC Workshop, Hinxton, UK, 2011.
- D. Campos, S. Matos, and J. L. Oliveira
“Annotating the CALBC corpus with a machine learning harmonization approach”
In Second CALBC Workshop, Hinxton, UK, 2011.
- L. Bastião, C. Costa, A. Silva, and J. L. Oliveira
“A PACS Gateway to the Cloud”
In 6th Iberian Conference on Information Systems and Technologies (CISTI 2011), Chaves, Portugal, 2011, pp. 519-524.
- J. Arrais and J. L. Oliveira
“Gene-disease prioritization through biomedical networks,” in 10th IEEE International Conference on Information Technology and Applications in Biomedicine (ITAB 2010), Corfu, Greece, 2010.
- P. Lopes, D. Campos, and J. L. Oliveira
“A tagging system for bioinformatics resources,” in 10th IEEE International Conference on Information Technology and Applications in Biomedicine (ITAB 2010), Corfu, Greece, 2010.
- J. Arrais and J. L. Oliveira
“On the exploitation of cloud computing in Bioinformatics,” in 10th IEEE International Conference on Information Technology and Applications in Biomedicine (ITAB 2010), Corfu, Greece, 2010.
- P. Lopes and J. L. Oliveira
“An extensible platform for variome data integration,” in 10th IEEE International Conference on Information Technology and Applications in Biomedicine (ITAB 2010), Corfu, Greece, 2010.
- L. S. Ribeiro, C. Costa, and J. L. Oliveira
“A Distributed and Reliable DICOM Storage Facility”
In 28th International EuroPACS Meeting (CARS 2010), Geneva, Switzerland, 2010.
- F. Martin-Sanchez, V. Lopez-Alonso, L. Salamanca, J. L. Oliveira, and E. Andres
“Managing Knowledge Related to the Clinical Relevance of Biomarkers: An Example in Parkinson’s Disease”
In 2010 AMIA Summit on Translational Bioinformatics, San Francisco, CA, USA, 2010.
- S. Matos, D. Campos, and J. L. Oliveira
“Vector-space models and terminologies in gene normalization and document classification”
In Proceedings of BioCreative III Workshop, Bethesda, Maryland, USA, September 2010
- S. Matos, J. Arrais, and J. L. Oliveira
“Expanding Gene-based PubMed Queries”
In 4th International Workshop on Practical Applications of Computational Biology and Bioinformatics (IWPACBB 2010), Guimarães, Portugal, 2010.
- J. Arrais, J. Pereira, P. Lopes, S. Matos, and J. L. Oliveira
“Improving cross mapping in biomedical databases”
In 4th International Workshop on Practical Applications of Computational Biology and Bioinformatics (IWPACBB 2010), Guimarães, Portugal, 2010.
- J. P. Lousado, J. L. Oliveira, G. Moura, and M. A. S. Santos
“An application for study tandem repeats in ortologous genes”
In 4th International Workshop on Practical Applications of Computational Biology and Bioinformatics (IWPACBB 2010), Guimarães, Portugal, 2010.
- P. Lopes and J. L. Oliveira
“A Holistic Approach for Integrating Genomic Variation Information”
In Xth Spanish Symposium on Bioinformatics (JBI2010), Malaga, Spain, 2010.
- J. P. Lousado, J. L. Oliveira, G. Moura, and M. A. S. Santos
“Análise da evolução de repetições de codões e de aminoácidos em dados biológicos”
In 5th Iberian Conference on Information Systems and Technologies (CISTI 2010), Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 2010.
- D. Campos, S. Matos, and J. L. Oliveira
“Recognition of gene/protein names using Conditional Random Fields”
In International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval (KDIR 2010), Valencia, Spain, 2010.
- L. S. Ribeiro, L. Bastião, C. Costa, and J. L. Oliveira
“Email-P2P Gateway to Distributed Medical Imaging Repositories”
In HEALTHINF 2010, Valencia, Spain, 2010.
- J. C. Santos, T. Pedrosa, C. Costa, and J. L. Oliveira
“Modelling a Portable Personal Health Record”
In HEALTHINF 2010, Valencia, Spain, 2010.
- T. Pedrosa, R. P. Lopes, J. C. Santos, C. Costa, and J. L. Oliveira
“Towards an EHR architecture for mobilde citizens”
In HEALTHINF 2010, Valencia, Spain, 2010.
- J. C. Santos, T. Pedrosa, C. Ferreira, C. Costa, and J. L. Oliveira
“Gathering and Managing Complementary Diagnostic Tests,” in 5th Iberian Conference on Information Systems and Technologies (CISTI 2010), Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 2010.
- L. S. Ribeiro, C. Costa, and J. L. Oliveira
“A Proxy of DICOM services”
In SPIE Medical Imaging 2010, S. Diego, CA, USA, 2010.
- J. Arrais, J. Pereira, J. Fernandes, and J. L. Oliveira
“GeNS: A Biological Data Integration Platform”
In World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology (WASET 2009), Venice, Italy, 2009, pp. 416 – 421.
- P. Lopes and J. L. Oliveira
“Cloud Computing and Digital Libraries : First Perspectives on a Future Technological Alliance ”
In 9ª Conferência da Associação Portuguesa de Sistemas de Informação (CAPSI 2009), Viseu, Portugal, 2009.
-
M. Pinheiro, M. J. Simões, C. Egas, and J. L. Oliveira
“Identifying SNPs candidates using 454 sequencing technology”
In Jornadas de Bioinformática (JB 2009), Lisbon, Portugal, 2009.
- P. Lopes, J. Arrais, and J. L. Oliveira
“Link Integrator: A Link-based Data Integration Architecture”
In International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval (KDIR 2009), Madeira, Portugal, 2009.
- P. Lopes, D. Pinto, D. Campos, and J. L. Oliveira
“Arabella: A Directed Web Crawler”
In International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval (KDIR 2009), Madeira, Portugal, 2009.
- T. Pedrosa, C. Costa, R. P. Lopes, and J. L. Oliveira
“Virtual Health Card System”
In Inforum 2009, Lisbon, Portugal, 2009.
- D. Polónia, C. Costa, J. L. Oliveira, and A. M. O. Duarte
“Inequality problems in the distribution of radiologists in Portugal: Requirements for the creation of an imaging marketplace”
In eChallenges 2009, Ankara, Turkey, 2009.
- P. Lopes, J. Arrais, and J. L. Oliveira
“A Client-side Workflow Management System”
In 3rd International Workshop on Practical Applications of Computational Biology and Bioinformatics(IWPACBB 2009), Salamanca, Spain, 2009.
- J. P. Lousado, G. Moura, M. A. S. Santos, and J. L. Oliveira
“Analysing the evolution of repetitive strands in genomes”
In 3rd International Workshop on Practical Applications of Computational Biology and Bioinformatics (IWPACBB 2009), Salamanca, Spain, 2009.
- S. Matos, A. Barreiro, J.L. Oliveira
“Syntactic Parsing for Bio-Molecular Event Detection from Scientific Literature”, 14th Portuguese Conference on Artificial Intelligence, EPIA 2009, Aveiro, Portugal, Oct. 2009.
- P. Lopes, J. Arrais and J. L. Oliveira
“Dynamic Service Integration using Web-based Workflows”
In 10th International Conference on Information Integration and Web Applications & Services“, Linz, Austria, Nov. 2008, pp. 622-625.
- D. Santos, C. Costa, J. L. Oliveira, and A. Neves
“Alternative lossless compression algorithms in X-ray cardiac images” in Computational Vision and Medical Image Processing, N. J. João Tavares, Ed. London: Taylor & Francis Group, 2008, pp. 143-146.
- D. Polónia, C. Costa, and J. L. Oliveira
“A Model to Optimize the Use of Imaging Equipment and Human Skills Scattered in Very Large Geographical Areas”
In 9th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2004), Madeira, Portugal, 2007.
- V. Afreixo, A. Freitas, M. Pinheiro, J. L. Oliveira, G. Moura, and M. A. S. Santos
“Exploiting a Biclustering algorithm in ORFeome analysis”
In Proceedings of the 2007 VLDB Workshop on Data Mining in Bioinformatics, Vienna, Austria, 2007.
- A. Freitas, J. Duarte, M. Pinheiro, J. L. Oliveira, G. Moura, and M. A. S. Santos
“Homo sapiens versus Pan troglodytes: quão diferentes são?” in Actas do XIV Congresso Nacional da Sociedade Portuguesa de Estatística, Covilhã, Portugal, 2007.
- J. Duarte, A. Freitas, M. Pinheiro, J. L. Oliveira, G. Moura, and M. A. S. Santos
“ISA: um algoritmo de bi-classificação?” in Actas do XIV Congresso Nacional da Sociedade Portuguesa de Estatística, Covilhã, Portugal, 2007.
- A. Freitas, M. Pinheiro, V. Afreixo, J. Duarte, J. L. Oliveira, G. Moura, and M. A. Santos
“A median-based Iterative Signature Algorithm”
In IASC 07 – Statistics for Data Mining, Learning and Knowledge Extraction, Aveiro, Portugal, 2007.
- A. Freitas, M. Pinheiro, J. L. Oliveira, G. Moura, and M. A. Santos
“A new limiting distribution for a statistical test for the homogeneity of two multinomial populations”
In Workshop in Statistic on Genomics and Proteomic, CIM, 2006.
- J. Arrais, D. Polónia, and J. L. Oliveira
“A prospective study on the integration of microarrays data in HIS/ERP”
In Biological and Medical Data Analysis (ISBMDA’ 2006), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol. 4345, Thessaloniki, Greece, 2006.
- D. Polónia, C. Costa, and J. L. Oliveira
“Optimizing PACS and imaging resources”
In The XX International Congress of the European Federation for Medical Informatics (MIE 2006), Maastricht, Netherlands, 2006.
- G. Dias, J. L. Oliveira, F. Vicente, and F. Martín-Sanchez
“Integrating Medical and Genomic Data: a Sucessful Example for Rare Diseases”
In The XX International Congress of the European Federation for Medical Informatics (MIE 2006), Maastricht, Netherlands, 2006.
- J. Arrais, J. L. Oliveira, G. Grimes, S. Moodie, K. Robertson, and P. Ghazal
“Microarray data sharing in BioMedicine”
In The XX International Congress of the European Federation for Medical Informatics (MIE 2006), Maastricht, Netherlands, 2006.
- D. Polónia, C. Costa, and J. L. Oliveira
“A PACS based GRID of resources”
In 4th International EuroPACS Conference (EuroPACS 2006), Trondheim, Norway, 2006.
- G. Dias, J. L. Oliveira, F. Vicente, and F. Martin-Sanchez
“Integration of Genetic and Medical Information Through a Web Crawler System”
In Biological and Medical Data Analysis (ISBMDA’ 2005), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol. 3745, Aveiro, Portugal, 2005.
- C. Costa, J. L. Oliveira, A. Silva, V. Ribeiro, and J. Ribeiro
“Data Management and Visualization Issues in a Fully Digital Echocardiography Laboratory”
In Biological and Medical Data Analysis (ISBMDA’ 2005), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol. 3745, Aveiro, Portugal, 2005.
- C. Costa, J. L. Oliveira, A. Silva, V. Ribeiro, and J. Ribeiro
“A Telemedicine Platform for Cardiovascular Ultrasound”
In The XIX International Congress of the European Federation for Medical Informatics (MIE 2005), Geneve, Switzerland, 2005.
- D. Polónia, C. Costa, and J. L. Oliveira
“Architecture evaluation for the implementation of a Regional Integrated Electronic Health Record”
In The XIX International Congress of the European Federation for Medical Informatics (MIE 2005), Geneve, Switzerland, 2005.
- M. Pinheiro, J. L. Oliveira, M. A. S. Santos, H. Rocha, M. L. Cardoso, and L. Vilarinho
“Results of a Biomedical Application in Newborn Screening Programs”
In The 3rd European Medical and Biological Engineering Conference (EMBEC 2005), Prague, Czech Republic, 2005.
- J. Arrais, L. Silva, M. Rodrigues, L. Carreto, J. L. Oliveira, and M. A. S. Santos
“Why Another Microarrays LIMS”
In The 3rd European Medical and Biological Engineering Conference (EMBEC 2005), Prague, Czech Republic, 2005.
-
D. Polónia, J. L. Oliveira, and N. P. Rocha
“Overview of information systems training in Portuguese medicine courses”
In Health and Medical Informatics Applications – Educational Aspects (EFMI-STC 2005), Athens, Greece, 2005.
-
D. Polónia and J. L. Oliveira
“Health Information Systems and Telematics: A best of breed evaluation framework for the Portuguese case”
In European Health Management Association Annual Conference 2005 (EHMA 2005), Barcelona, Spain, 2005.
-
F. Vicente, I. Hermosilla, M. García-Remesal, D. Pérez del Rey, B. Romero, I. Oliveira, J. L. Oliveira, A. S. Pereira, and F. Martin-Sanchez
“Infogenmed: Un Laboratorio Virtual para la Integración de Información Clínica y Genética en Aplicaciones Médicas”
In VII Congreso Nacional de Informático de la Salud (Inforsalud 2004), Madrid, Spain, 2004.
-
Oliveira, J. L. Oliveira, F. Martin-Sanchez, V. Maojo, and A. S. Pereira
“Biomedical information integration for health applications with Grid: a requirements perspective”
In Healthgrid 2004, Clermont-Ferrand, France, 2004.
-
D. Polónia, J. L. Oliveira, and M. O. Duarte
“Information Systems (IS) in the Third and Fourth Generation Mobile Operator”
In 5ª Conferência da Associação Portuguesa de Sistemas de Informação (CAPSI 2004), Lisbon, 2004.
-
C. Costa, A. Silva, J. L. Oliveira, V. Ribeiro, and J. Ribeiro
“Himage PACS: A new approach to storage, integration and distribution of cardiologic images”
In Progress in Biomedical Optics and Imaging, vol. 5, H. H. Ratib OM, Ed., SPIE, 2004, pp. 277-287.
-
M. Pinheiro, J. L. Oliveira, M. A. S. Santos, H. Rocha, M. L. Cardoso, and L. Vilarinho
“NeoScreen: A software application for MS/MS newborn screening analysis”
In International Symposium on Biological and Medical Data Analysis (ISBMDA 2004), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol. 3337, Barcelona, Spain, 2004.
-
J. L. Oliveira, G. Dias, I. Oliveira, P. Rocha, I. Hermosilla, F. Vicente, I. Spiteri, F. Martin-Sanchez, and A. S. Pereira
“DiseaseCard: a web-based tool for the collaborative integration of genetic and medical information”
In Biological and Medical Data Analysis (ISBMDA 2004), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol. 3337, Barcelona, Spain, 2004.
-
D. Polónia, I. Oliveira, and J. L. Oliveira
“A Business Process Model for Public Health Information Systems: A Governmental Perspective”
In 6th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2004), Porto, Portugal, 2004.
-
C. Costa, J. L. Oliveira, and A. Silva
“E-Services in Mission-Critical Organizations: Identification Enforcement”
In 6th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2004), Porto, Portugal, 2004.
-
M. García-Remesal, V. Maojo, H. Billhardt, J. Crespo, R. Alonso-Calvo, D. Pérez, F. Martín, V. López, J. Sánchez, F. Vicente, M. García-Rojo, A. Gómez de la Cámara, A. Sousa, J. L. Oliveira, I. Oliveira, M. Santos, and A. Babic
“Designing New Methodologies for Integrating Biomedical Information in Clinical Trials”
In EuroMISE 2004, Prague, Czech Republic, 2004.
-
C. Costa, A. Silva, J. L. Oliveira, A. S. Pereira, and V. Ribeiro
“A New Concept for an Integrated Healthcare Access Model”
In Medical Informatics Europe (MIE 2003), Saint Malo, France, 2003.
-
C. Costa, J. L. Oliveira, and A. Silva
“Authentication Model to Enforce Network Entities Identification”
In 4rd Conference on Telecommunications (ConfTele 2003), Aveiro, Portugal, 2003.
-
C. Costa, J. L. Oliveira, A. Silva, and V. Gama
“An Integrated Access Interface to Multimedia EPR”
In 21st International EuroPACS Meeting (EuroPACS 2003), London, United Kingdom, 2003.
-
Oliveira, J. L. Oliveira, M. Santos, F. Martin-Sanchez, and A. S. Pereira
“On the requirements of biomedical information tools for health applications: the INFOGENMED case study”
In 7th Portuguese Conference on Biomedical Engineering (BioEng 2003), Lisbon, Portugal, 2003.
-
C. Costa, J. L. Oliveira, and A. Silva
“Electronic Patient Record Virtually Unique based on a Crypto Smart Card”
In International Conference on Web Engineering (ICWE 2003), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol. 2722, Oviedo, Spain, 2003.
-
C. Costa, J. L. Oliveira, and A. Silva
“Critical Information Systems Authentication based on PKC and Biometrics”
In International Conference on Web Engineering (ICWE 2003), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol. 2722, Oviedo, Spain, 2003.
-
C. Costa, J. L. Oliveira, and A. Silva
“A User-Oriented Model to Manage Multiple Digital Credentials”
In IEEE 5th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2003), Angers, France, 2003.
-
J. C. Santos, J. L. Oliveira, and C. Costa
“A User-oriented Multi-service Access Control System”
In 5ª Conferência sobre Redes de Computadores (CRC 2002), Faro, Portugal, 2002.
-
C. Costa, J. L. Oliveira, and A. Silva
“A Trusted Brokering Service for PKI Interoperability and Thin-Clients Integration”
In IEEE Third International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2001), Setúbal, Portugal, 2001.
-
C. Costa, J. L. Oliveira, and A. Silva
“Um Novo Mecanismo de Autenticação para Sistemas de Informação Clínica” (in portuguese)
In 4ª Conferência sobre Redes de Computadores (CRC 2001), Covilhã, Portugal, 2001.

 About
About Citation
Citation Download
Download





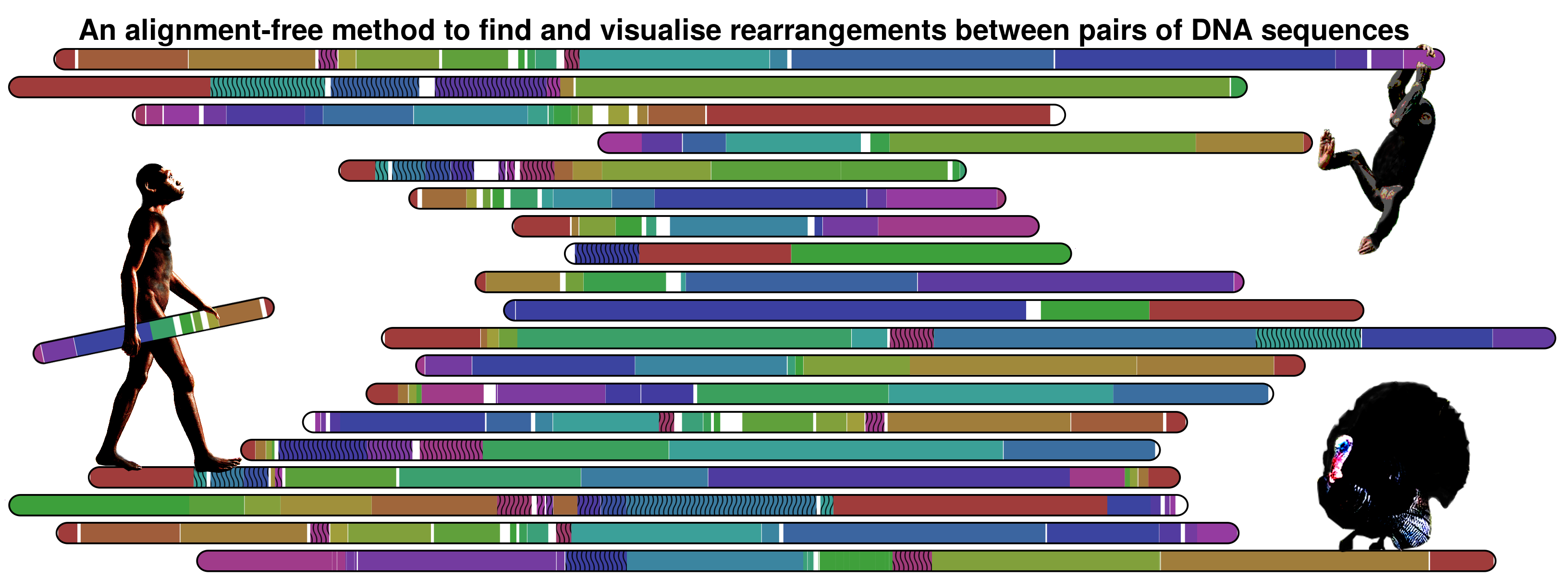







 DNAatGlance is a program for the detection of large-scale genomic regularities by visual inspection. Several discovery strategies are possible, including the standalone analysis of single sequences, the comparative analysis of sequences from individuals from the same species, and the comparative analysis of sequences from different organisms. The software was designed and implemented at
DNAatGlance is a program for the detection of large-scale genomic regularities by visual inspection. Several discovery strategies are possible, including the standalone analysis of single sequences, the comparative analysis of sequences from individuals from the same species, and the comparative analysis of sequences from different organisms. The software was designed and implemented at